In February 2024, the “Expert Consensus on Imaging Patterns and Applications of Advanced Age-Related Macular Degeneration (2024)” (hereinafter referred to as the Expert Consensus) was formally published in the Chinese Journal of Experimental Ophthalmology. Bigvision Medical founder Professor Chen Xinjian, from SOOCHOW University, participated in the formulation as an expert in ophthalmic imaging and artificial intelligence. The Expert Consensus systematically discusses various imaging patterns of advanced AMD, evaluates the advantages and disadvantages of each imaging pattern based on the principles and clinical practices of different detection methods, and provides a systematic summary of the role of each imaging pattern in future research on advanced AMD.

Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), also known as senile macular degeneration, refers to the age-related changes in the structure of the macular region. Its onset is related to the metabolic decline of retinal pigment epithelial cells. AMD mostly occurs in individuals aged 45 and above, with its prevalence increasing with age. The “Expert Consensus” points out that advanced AMD is a mid-to-late stage change in the pathology, characterized by atrophy and thinning of the outer retina, loss of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), and the presence of choroidal neovascularization, including geographic atrophy and wet AMD. It seriously affects the central vision of patients.
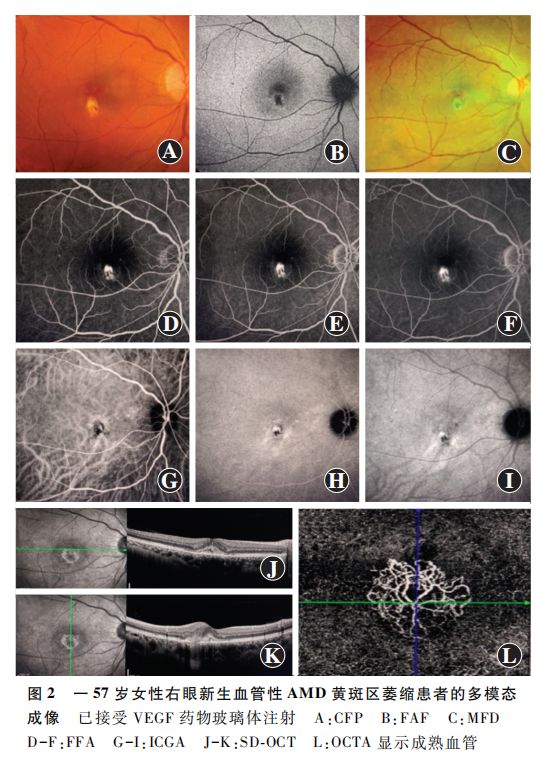
When patients suffer from such retinal diseases, the optimal selection of retinal imaging patterns is crucial for the diagnosis, evaluation, quantification analysis, and treatment monitoring of advanced AMD, and may affect the timeliness and cost of related clinical diagnosis and treatment. The expert group pointed out that multimodal imaging is currently the best method for detecting, quantifying, and monitoring advanced AMD. For patients with suspected AMD at their initial visit, it is recommended to use color fundus photography (CFP), optical coherence tomography (OCT), and OCT angiography (OCTA) for disease screening.

OCT is a non-contact, non-invasive, high-resolution retinal examination technique. OCT examination not only helps in staging AMD but also reflects the prognosis of the disease to some extent. The Bigvision fully automatic AI OCT BV1000 series can accurately capture the subtle morphology of retinal lesions, including 16 major retinal lesions such as macular holes, epiretinal membranes, cystoid macular edema, vitreomacular traction, and choroidal neovascularization, providing a basis for further diagnosis. In addition, Bigvision’s self-developed image-assisted diagnosis software MIAS-3000, using advanced AI medical imaging algorithm models, can automatically assist in the diagnosis of AMD, realizing early detection, early treatment, and early diagnosis of AMD. Currently, the product has completed clinical trials and is expected to become the world’s first OCT image-assisted diagnostic system with Class III certification.

Driven by scientific research to promote medical innovation and further advance the integration of medicine and engineering, solving real-world clinical problems is the tireless pursuit of Bigvision Medical. It is believed that in the future, the BiGway fully automatic AI OCT, coupled with the AI precision analysis assistance system, will assist in early detection of various retinal diseases, including macular degeneration, building a robust defense line for eye disease screening.









No comments yet.